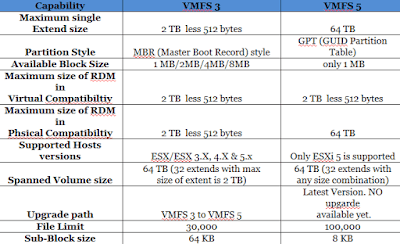
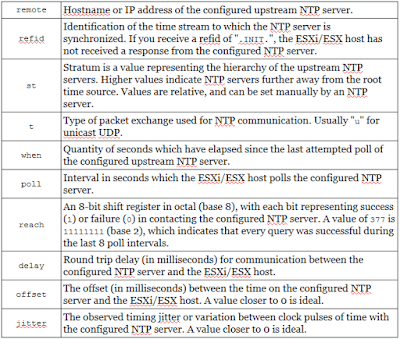
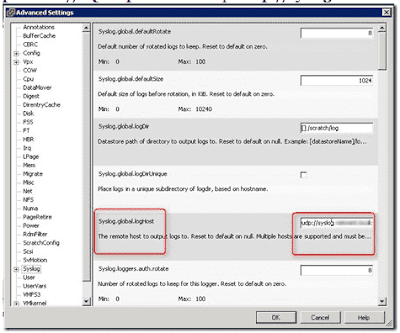
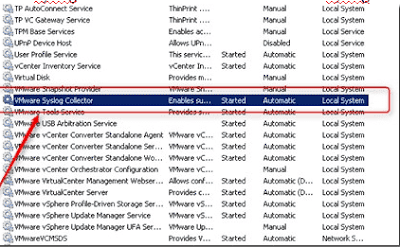
Whenever you find below Symptoms
Cannot run the host on Hewlett Packard (HP) hardware
Running the host on HP hardware fails with a purple diagnostic screen
You see the error:
hpsa_update_scsi_devices@<None>#<None>+0x39c
hpsa_scan_start@<None>#<None>+0x187
hpsa_kickoff_rescan@<None>#<None>+0x20f
kthread@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x185
LinuxStartFunc@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x97
vmkWorldFunc@vmkernel#nover+0x83
CpuSched_StartWorld@vmkernel#nover+0xfa
Your host fails with a purple diagnostic screen and you see the error:
Panic: 892: Saved backtrace: pcpu X TLB NMI
_raw_spin_failed@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x5
detect_controller_lockup_thread@#+0x3a9
kthread@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x185
LinuxStartFunc@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x97
vmkWorldFunc@vmkernel#nover+0x83
CpuSched_StartWorld@vmkernel#nover+0xfa
PCPU X locked up. Failed to ack TLB invalidate (total of 1 locked up, PCPU9s): X)
Before host becomes unresponsive, in the /var/log/vmkernel.log file, you see entries similar to:
WARNING: LinDMA: Linux_DMACheckConstraints:149: Cannot map machine address = 0xfffffffffff, length = 49160 for device 0000:03:00.0; reason = buffer straddles device dma boundary (0xffffffff)WARNING: Heap: 4089: Heap_Align(vmklnx_hpsa, 32768/32768 bytes, 8 align) failed. caller: 0x41802dcb1f91cpu4:1696102)<4>hpsa 0000:09:00.0: out of memory in adjust_hpsa_scsi_table
Before you see a purple diagnostic screen, in the /var/log/vmkernel.log file, you see entries similar to:
Note: These are multiple memory error messages from the hpsa driver.
out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
WARNING: Heap: 3622: Heap vmklnx_hpsa (39113576/39121768): Maximum allowed growth (8192) too small for size (20480)
cpu7:1727675)<4>hpsa 0000:06:00.0: out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
cpu2:1727677)<4>hpsa 0000:0c:00.0: out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
cpu4:1727676)<4>hpsa 0000:09:00.0: out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
cpu3:1727738)WARNING: LinDMA: dma_alloc_coherent:726: Out of memory
cpu3:1727738)<3>hpsa 0000:06:00.0: cmd_special_alloc returned NULL!
Resolution should be
This is a known issue affecting VMware ESXi 5.x.
To resolve this issue, apply the updated driver supplied by HP. Always check the HCL to determine the latest available driver update.
Note: For all BL685c G7 blades and DL360p Gen8 servers, HP recommends to update to ESXi 5.5 update1 to the June 2014 version. For more information, see
The reasons for the recommendation are:
Fix for smx-provider memory leak issue is resolved.
Several issues for the hpsa driver are resolved in the .60 version found in new June 2014 version of ESXi 5.5 update1. The previous version of the hpsa driver was .50 and was problematic.
For the DL360p Gen8 servers, the iLO firmware need to be checked. If the iLO Firmware is not at 1.51, it is recommended to update the Firmware on all servers to 1.51. This is a critical update to avoid NMI events which would cause PSOD in your environment.
It is also recommended to check the DL360p Gen8 servers to make sure that they are at least at Feb 2014 system ROM. This is to correct a possible IPMI issue.
If this issue persists after the driver upgrade:
Open a HP Support Request, reference HP case 4648045806.
If this issue persists, open a support request with VMware Support.
Provide VMware support your HP case number.
Cannot run the host on Hewlett Packard (HP) hardware
Running the host on HP hardware fails with a purple diagnostic screen
You see the error:
hpsa_update_scsi_devices@<None>#<None>+0x39c
hpsa_scan_start@<None>#<None>+0x187
hpsa_kickoff_rescan@<None>#<None>+0x20f
kthread@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x185
LinuxStartFunc@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x97
vmkWorldFunc@vmkernel#nover+0x83
CpuSched_StartWorld@vmkernel#nover+0xfa
Your host fails with a purple diagnostic screen and you see the error:
Panic: 892: Saved backtrace: pcpu X TLB NMI
_raw_spin_failed@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x5
detect_controller_lockup_thread@#+0x3a9
kthread@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x185
LinuxStartFunc@com.vmware.driverAPI#9.2+0x97
vmkWorldFunc@vmkernel#nover+0x83
CpuSched_StartWorld@vmkernel#nover+0xfa
PCPU X locked up. Failed to ack TLB invalidate (total of 1 locked up, PCPU9s): X)
Before host becomes unresponsive, in the /var/log/vmkernel.log file, you see entries similar to:
WARNING: LinDMA: Linux_DMACheckConstraints:149: Cannot map machine address = 0xfffffffffff, length = 49160 for device 0000:03:00.0; reason = buffer straddles device dma boundary (0xffffffff)WARNING: Heap: 4089: Heap_Align(vmklnx_hpsa, 32768/32768 bytes, 8 align) failed. caller: 0x41802dcb1f91cpu4:1696102)<4>hpsa 0000:09:00.0: out of memory in adjust_hpsa_scsi_table
Before you see a purple diagnostic screen, in the /var/log/vmkernel.log file, you see entries similar to:
Note: These are multiple memory error messages from the hpsa driver.
out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
WARNING: Heap: 3622: Heap vmklnx_hpsa (39113576/39121768): Maximum allowed growth (8192) too small for size (20480)
cpu7:1727675)<4>hpsa 0000:06:00.0: out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
cpu2:1727677)<4>hpsa 0000:0c:00.0: out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
cpu4:1727676)<4>hpsa 0000:09:00.0: out of memory at vmkdrivers/src_9/drivers/hpsa/hpsa.c:3562
cpu3:1727738)WARNING: LinDMA: dma_alloc_coherent:726: Out of memory
cpu3:1727738)<3>hpsa 0000:06:00.0: cmd_special_alloc returned NULL!
Resolution should be
This is a known issue affecting VMware ESXi 5.x.
To resolve this issue, apply the updated driver supplied by HP. Always check the HCL to determine the latest available driver update.
Note: For all BL685c G7 blades and DL360p Gen8 servers, HP recommends to update to ESXi 5.5 update1 to the June 2014 version. For more information, see
The reasons for the recommendation are:
Fix for smx-provider memory leak issue is resolved.
Several issues for the hpsa driver are resolved in the .60 version found in new June 2014 version of ESXi 5.5 update1. The previous version of the hpsa driver was .50 and was problematic.
For the DL360p Gen8 servers, the iLO firmware need to be checked. If the iLO Firmware is not at 1.51, it is recommended to update the Firmware on all servers to 1.51. This is a critical update to avoid NMI events which would cause PSOD in your environment.
It is also recommended to check the DL360p Gen8 servers to make sure that they are at least at Feb 2014 system ROM. This is to correct a possible IPMI issue.
If this issue persists after the driver upgrade:
Open a HP Support Request, reference HP case 4648045806.
If this issue persists, open a support request with VMware Support.
Provide VMware support your HP case number.