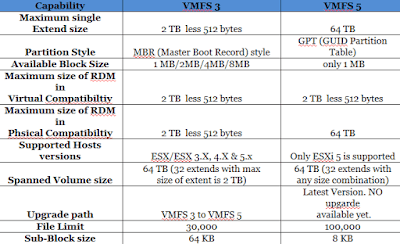
Differences between upgraded and newly created VMFS-5 datastores:
Based on the information above, the best approach to migrate to VMFS-5 is to create net new VMFS-5 datastores if you have the extra storage space, can afford the number of Storage vMotions required, and have a VAAI capable storage array holding existing datastores with 2, 4, or 8MB block sizes.
- VMFS-5 upgraded from VMFS-3 continues to use the previous file block size which may be larger than the unified 1MB file block size. Copy operations between datastores with different block sizes won’t be able to leverage VAAI. This is the primary reason I would recommend the creation of new VMFS-5 datastores and migrating virtual machines to new VMFS-5 datastores rather than performing in place upgrades of VMFS-3 datastores.
- VMFS-5 upgraded from VMFS-3 continues to use 64KB sub-blocks and not new 8K sub-blocks.
- VMFS-5 upgraded from VMFS-3 continues to have a file limit of 30,720 rather than the new file limit of > 100,000 for newly created VMFS-5.
- VMFS-5 upgraded from VMFS-3 continues to use MBR (Master Boot Record) partition type; when the VMFS-5 volume is grown above 2TB, it automatically switches from MBR to GPT (GUID Partition Table) without impact to the running VMs.
- VMFS-5 upgraded from VMFS-3 will continue to have a partition starting on sector 128; newly created VMFS-5 partitions start at sector 2,048.
Based on the information above, the best approach to migrate to VMFS-5 is to create net new VMFS-5 datastores if you have the extra storage space, can afford the number of Storage vMotions required, and have a VAAI capable storage array holding existing datastores with 2, 4, or 8MB block sizes.